【论文分享】用于社交网络中影响力最大化的多转换进化框架
A Multi-Transformation Evolutionary Framework for Influence Maximization in Social Networks
Recently, we have one paper entitled “A Multi-Transformation Evolutionary Framework for Influence Maximization in Social Networks” accepted by the IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine.
The IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine (CIM) publishes peer-reviewed articles that present emerging novel discoveries, important insights, or tutorial surveys in all areas of computational intelligence design and applications, in keeping with the Field of Interest of the IEEE Computational Intelligence Society (IEEE/CIS).
| Author | Chao Wang; Jiaxuan Zhao; Lingling Li; Licheng Jiao*; Jing Liu; Kai Wu |
|---|---|
| Affiliations | Xidian University |
| Emails | xiaofengxd@126.com (Dr. Chao Wang) |
| Paper | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10026148 |
| Code | https://github.com/xiaofangxd/MTEFIM |
Abstract
Influence maximization is a crucial issue for mining the deep information of social networks, which aims to select a seed set from the network to maximize the number of influenced nodes. To evaluate the influence spread of a seed set efficiently, existing studies have proposed transformations with lower computational costs to replace the expensive Monte Carlo simulation process. These alternate transformations, based on network prior knowledge, induce different search behaviors with similar characteristics to various perspectives. Specifically, it is difficult for users to determine a suitable transformation a priori. This article proposes a multi-transformation evolutionary framework for influence maximization (MTEFIM) with convergence guarantees to exploit the potential similarities and unique advantages of alternate transformations and to avoid users manually determining the most suitable one. In MTEFIM, multiple transformations are optimized simultaneously as multiple tasks. Each transformation is assigned an evolutionary solver. Three major components of MTEFIM are conducted via: 1) estimating the potential relationship across transformations based on the degree of overlap across individuals of different populations, 2) transferring individuals across populations adaptively according to the inter-transformation relationship, and 3) selecting the final output seed set containing all the transformation’s knowledge. The effectiveness of MTEFIM is validated on both benchmarks and real-world social networks. The experimental results show that MTEFIM can efficiently utilize the potentially transferable knowledge across multiple transformations to achieve highly competitive performance compared to several popular IM-specific methods.
Framework:
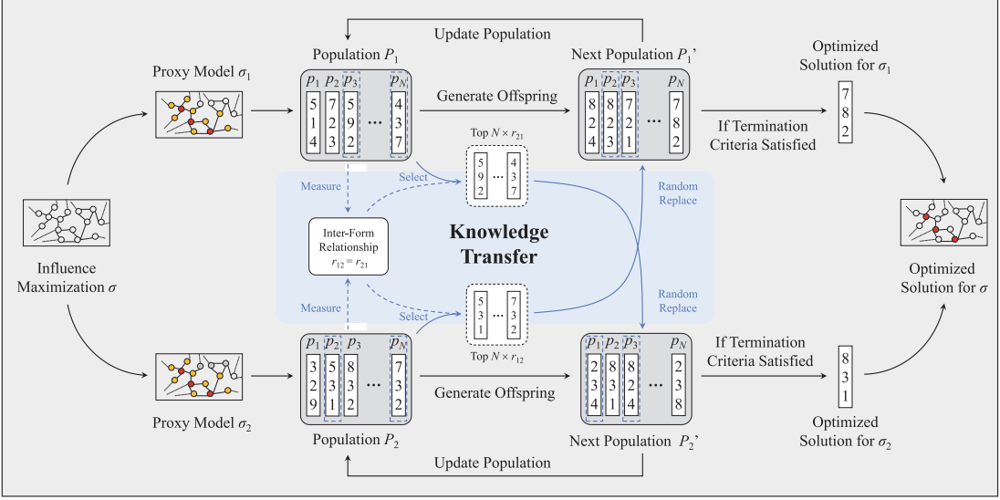
The outline of MTEFIM for bi-transformation IM.
Datasets:
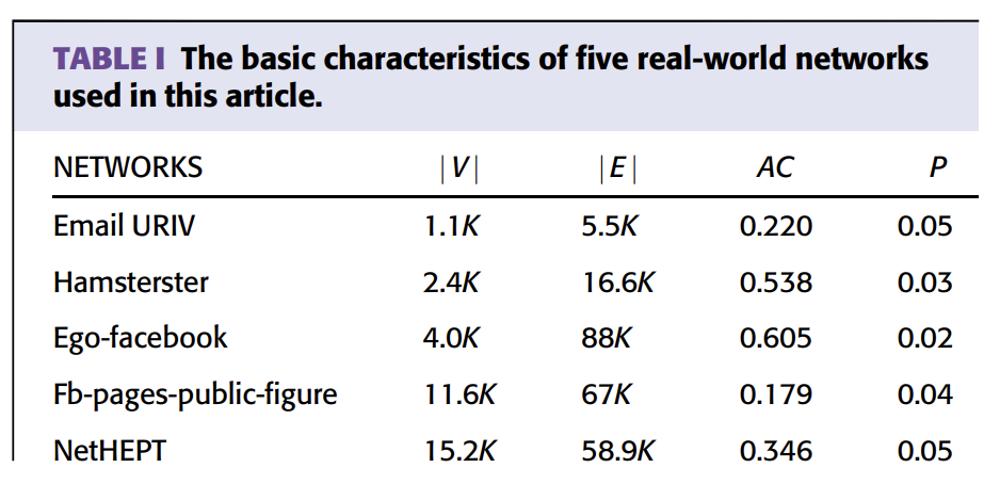
Datasets.
Results:
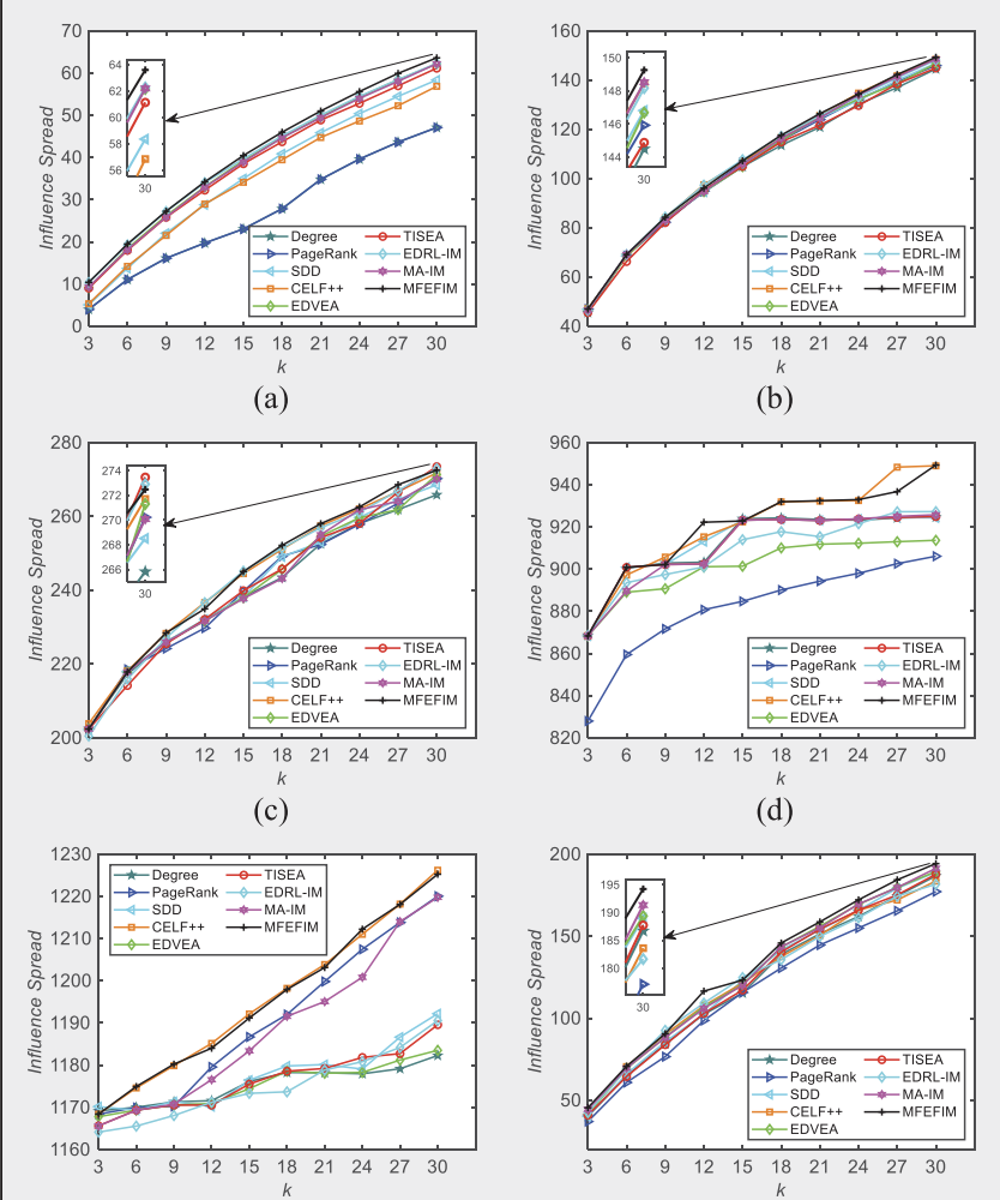
Influence spread obtained by different methods for IM on both the GN benchmark network and real-world social networks. (a) GN Network, (b) Email URIV, (c) Hamsterster, (d Ego-facebook, (e) Fbpages-public-figure, and (f) NetHEPT.
Citation:
@ARTICLE{10026148,
author={Wang, Chao and Zhao, Jiaxuan and Li, Lingling and Jiao, Licheng and Liu, Jing and Wu, Kai},
journal={IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine},
title={A Multi-Transformation Evolutionary Framework for Influence Maximization in Social Networks},
year={2023},
volume={18},
number={1},
pages={52-67},
doi={10.1109/MCI.2022.3222050}}